Back to top of the page
ABOUT ME
I am Dr. Hang Cui, a robotics engineer at Gatik AI Inc. Previously, I worked as a software engineer at the Center for Autonomy at the University of Illinois Urbana-Champaign.
Contact: Email
Follow me from below:
LinkedIn | Gitea | GitHubPROFICIENT IN
-
BLOGS
Communication Interfaces
Control Interfaces (Motion)
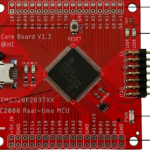
TI C2000 Real-time MCU
STM32 MCU with FreeRTOS
Simulink Embedded Coder
Yocto Project on Raspeberry Pi
SELF-HOSTED APPS
Gitea & CI Runner
Daily Notes
Brainstorm Mapping
Shared Markdown Notes
Bookmark Management
Project Management
Document Management
eBook Management
n8n AI Workflow Automation
-
RECENT POST
- TI C2000 MCU: 03 Pulse-Width Modulation
- TI C2000 MCU: 02 General-Purpose I/O (GPIO) and PinMux
- Ethernet Media Access Controller (Ethernet)
- TI C2000 MCU: 01 Introduction to Real-Time MCU
- Universal Serial Bus (USB)
- Local Interconnect Network (LIN)
- CAN Flexible Data-Rate (CAN-FD)
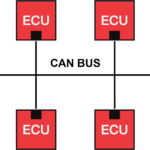
- Controller Area Network (CAN)
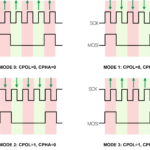
- Serial Peripheral Interface (SPI)
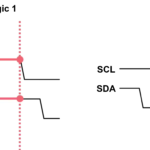
- Inter-Integrated Circuit (I2C)
VISITOR MAP